JavaScript Callbacks: A Beginner's Guide
Callbacks are a fundamental concept in JavaScript that every developer should know. In this guide, we'll explore what callbacks are, how they work, and provide an example to help you understand how to use them in your own code.
What are Callbacks?
In JavaScript, a callback is a function that is passed as an argument to another function and is executed by that function when a certain event occurs or a certain task is completed. The idea behind callbacks is to allow the function that receives them to perform some additional processing after the task is completed or the event has occurred.
How do Callbacks work?
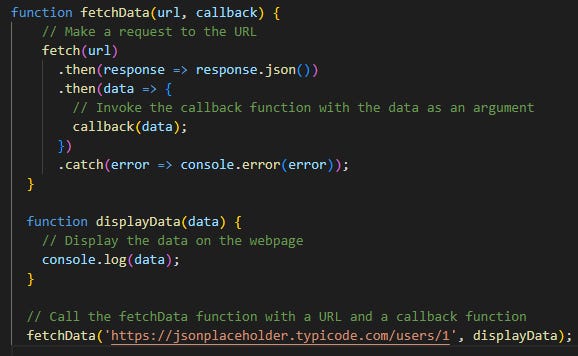
Callbacks work by passing a function as an argument to another function. The receiving function then executes the callback function when it has completed its task. Here's an example:
In this example, the fetchData function takes two arguments: a URL to fetch data from, and a callback function to invoke with the data when the request is complete. The fetchData function uses the fetch API to make a request to the specified URL, and then parses the response as JSON data.
Once the data has been obtained, the callback function is invoked with the data as an argument. In this case, the displayData function is passed as the callback function, which simply logs the data to the console.
Why use Callbacks?
Callbacks are commonly used in asynchronous programming to handle events or perform additional processing after a task has been completed. By passing a function as an argument, you can customize the behavior of a function without modifying its code directly.
Callbacks also provide a way to write modular code, as functions can be composed and reused with different callbacks to achieve different behaviors. This makes code more maintainable and easier to read.
Conclusion
Callbacks are an important concept in JavaScript that allow you to handle events and perform additional processing after a task has been completed. By passing a function as an argument to another function, you can customize the behavior of a function without modifying its code directly. Callbacks are commonly used in asynchronous programming and provide a way to write modular and maintainable code.
In the example we looked at, the fetchData function takes a callback as an argument and invokes it with data when the request is complete. By passing different callbacks, we could display the data differently, store it in a database, or perform any other type of processing we want.
I hope this guide has helped you understand callbacks and how to use them in your own code. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to leave a comment below.